Parts of a Mountain Bike Which we will talk about,let us firstly get to know the types of mountain bikes.
1.What kinds of mountain bikes are there?
Ordinary off-road XC (Cross Country)– cross country mountain bike
Mild off-road models, with strong climbing performance, are used for ordinary mountain off-road, and are also the lightest and most practical models in mountain bikes. They pursue light weight and high-speed passability, so new models are mostly 29-inch large wheel diameters. . Most of them are hard frames, and the fork travel is 80-120mm.
Buy the most hot selling mountain bike
Lindau TR (Trail)
Most of the riding routes are forest trails, hence the name, focusing on the smoothness of riding. Most of them are full-suspension models, and the travel is mostly 140mm front and rear.
All Mountain AM (All Mountain)
The vehicle is average in performance, capable of continuous climbs or descents, but not specialized, and is the best choice for those who just want to own a car but can ride more terrain or want to go on long off-road trips. 150-160mm front and rear travel.
Dual Slalom DS (Dual Slalom)
Two-person curved track racing vehicles, because of the emphasis on high-speed cornering, jumping, and pumping (a technique for accelerating through terrain), the vehicles are mostly short-form or medium-travel, and are transformed from soil slopes, forest roads, AM, FR vehicles. Come.
Free Ride FR (Free Ride)
A kind of skillful riding that is not bound by terrain restrictions, swept the American car industry around 05 to 10 years, and produced a large number of highly skilled freeriders. Tends to be high-speed and high-intensity, and uses natural terrain or artificially constructed jumping platforms to make great leaps, and likes various stunts in the air, with a stroke of 180-200mm.
Dirt Jumping
With the help of artificially constructed venues for aerial leaps and stunts, the vehicles are mostly hard tails and short rear forks, emphasizing strength and geometric angles, and the frames are mostly co-mo steel, which has a larger space for the ride. 135*10mm rear wheel, front fork travel less than 100mm.
Mountain Bike
Downhill DH (Down Hill)
Focus on downhill and big drop, use double-shoulder front forks, high frame strength, the weight of the whole vehicle is more than 17KG, there is a large preload, and the stroke is 200-203mm.
2.What are the parts to a mountain bike?
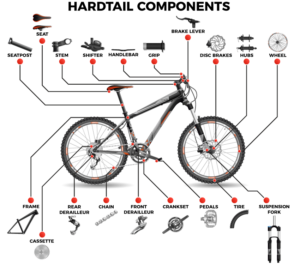
Frame
Whether a mountain bike is comfortable to ride, whether it is light and easy to control, how strong it can withstand, how long it can be used, whether it can be upgraded, etc., the key is to look at the frame.
The frame is roughly divided into two types: hard tail frame, full suspension frame (soft tail frame).
Briefly talk about the choice of frame size: Generally, the frame is selected according to the height, and it is very important to choose the frame that suits you!
Frame and height reference data:
14 inch-150-160 15 inch-155-165
16 inch-160-170 17 inch-165-175
18 inch-170-180 19 inch-175-185
20 inch-180-190 21 inch-185-195
Before 2009, almost all mountain bikes were 26-inch. Until 2009, MARMOT Groundhog Bicycle Company developed the world’s first 27.5-inch/650B bike in Washington, USA. Because this model has the best handling, stability, safety and best performance for the bicycle, since then, the new wheel diameter revolution in the bicycle industry has officially arrived, and major brands have followed suit to develop this size vehicle, 27.5 The inch/650B vehicle has gradually become the mainstream product in the bicycle market.
Because everyone’s body proportions are different, legs and arms are different, I will teach you one of the simplest and most practical actual measurement methods: wearing your shoes, standing on the frame across the frame, with feet shoulder-width apart , there should be a distance of about 5-6 cm between the crotch and the top tube of the frame; if the top tube is close to or next to the crotch, the frame is too large, and if the top tube is too far from the crotch, the frame is small. Those who like off-road should choose a smaller one, and the distance between the crotch and the upper tube of the frame should be about 6-10 cm. In this way, the handling is good and the safety is high, because off-road is more dangerous, so the frame should be smaller.

Hardtail frame
Less effort to ride, lighter and less expensive, a frame around 2000 RMB would be nice.
Hardtails, as the name suggests, don’t have rear shocks, but most have shock-absorbing front forks. A few years ago, choosing between the two was simple: people generally bought hardtail mountain bikes. With the development of rear shock absorption technology, it is difficult to decide whether to buy a hardtail mountain bike or a full shock mountain bike. While full-shock mountain bikes have improved a lot, hardtail mountain bike technology has also evolved. The choice between a hardtail or a full-shock mountain bike depends on what you plan to ride—are you going to race off-road, all-mountain trails or smooth nature exploration? As a rule of thumb, the more technical the terrain you plan to traverse, the more likely you will need a hardtail mountain bike.
Hardtail mountain bikes are ideal for off-highway terrain, one-way trails and competition. It is lighter, more durable and less expensive than a full-shock mountain bike. Lighter because there are fewer parts on the frame, and more durable because it has no pivot or rear shock to service. That means it requires less maintenance, so it’s cheaper to use and less expensive to buy initially. For these reasons, hardtail mountain bikes have always been the choice of many off-road competitors. Whether you’re new to mountain biking or a seasoned veteran, hardtail mountain bikes are great track bikes. In fact, if you’ve ever ridden a hardtail mountain bike, you’ll likely agree that it does handle most terrain.
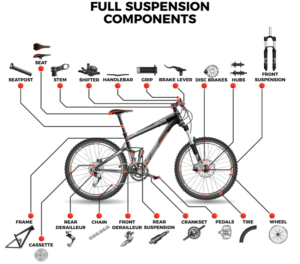
Soft tail frame
Also known as a full-shock frame, it is more comfortable, and you don’t need to slow down when crossing bumpy mountain roads, but you can ride tirelessly, not suitable for long distances, and the price is high, especially if you choose an excellent rear shock absorber, the price is the same as the frame. Prices are comparable.
Frame type
There are so many types of frame structures on the market, and each brand is slightly different, but they can be roughly divided into the following three types, and there are other sub-types under each category, which we will talk about include:
Fixed pivot a. Single rocker arm (Monopivot) b. Link type (Fauxbar)
Virtual Transfer Point a. Horst link b. VPP c. NRS d. Lawwill e.abp
Others a. URT b. i-Drive c.app
The effect of pedaling on the suspension frame
The most interesting thing about the shock absorber frame is the response to the pedaling force. Since the front triangle and the rear triangle of the shock absorber frame are separated, the pedaling force may cause the shock absorber to compress or stretch and generate energy. Loss, and we call this situation ‘Bobbing’ (although someone has translated this term, but I don’t think the translation is good, so I use the original). The advanced frame design is to achieve that the shock absorber does not respond to the pedaling force. At this time, we call the response of the frame to the pedaling ‘neutral (neutral)’.
Mountain bike seat cushion
Everyone’s body length, hand length, and foot length are different. Even if you buy a bicycle of the right size, it does not mean that the bicycle is really suitable. In fact, just take a little time to make adjustments by referring to the following simple “set-up steps”.
Cushion angle
First, adjust the easiest seat angle first. The angle of the seat cushion should generally be kept horizontal. Since most of the cushion surfaces of the seat cushions on the market are curved surfaces, visual inspection may not be accurate, so you can first place a long ruler on the seat cushion, and then use your eyes to visually grasp the level. That’s a lot easier.
But the angle of the seat cushion is by no means rigid. For example, some people often complain of crotch pain after riding a bike, which may be caused by too much pressure on the front of the seat cushion. This is to adjust the nose end of the seat cushion a little bit down, which can reduce the pressure on the crotch area. pressure, especially when going uphill. On the contrary, some people do not ride uphill for a long time, but like the fun of rushing down and breaking. When rushing downhill, because of the need to control the center of gravity, the rider often moves back and forth between the seat cushion and the rear of the seat cushion. It’s best to tilt the nose of the saddle up a few degrees and lower the seat tube height to help your body move on the saddle when going downhill.
Front fork
The front fork is a high-tech component in mountain bikes. Mountain bikes with hard front forks are rare, and they are basically front forks with shock absorbers. There are several factories in the world with good front forks: RST, SR Suntour, DNM, RockShox, Marzocchi, Manitou, FOX, BOS… Among them, the forks of the first five factories are popular below 1,000 yuan Model fork, and the latter two are rare, and the price is too high. Even the popular fork is close to 2,000 yuan, which is unbearable for newcomers, and it is difficult to play its effect after buying it.
Types of media for forks:
⑴, spring fork: the lowest fork, no damping.
Features: Cheap, you can buy a good one for 300 yuan.
(2) Resistance fork: The resistance fork is used as the medium, and there is no damping.
Features: It is less than the previous and more than the bottom, but the resistance fork will age after three years and needs to be replaced.
(3) Oil spring fork: The spring (Coil) is used as the rebound medium, and the oil is used as the damping.
Features: The heaviest, but the strongest. The spring is relatively moist to use and is sensitive to small vibrations. Generally, the shock absorber oil is changed every six months, and the fork is removed to change the oil.
⑷. Oil and gas fork: Air (Air) is used as the rebound medium, and shock oil is used as the damping.
Features: Lighter than oil spring forks, but less rigid. (It won’t be too low. Ordinary off-road is enough.) Once every six months, the car dealer will provide a special pump for free. You can also buy it separately, with a pressure gauge for about 200 yuan. The advantage of using air as a medium is that it is lighter in weight, which can protect the rider’s wrist in high-speed off-road, but it is less responsive to small shocks.
The working sequence of the front fork should be: encountering an obstacle – the front fork is compressed – to the extreme – rebounded to the original length (the speed of the rebound is affected by the damping) – the work of the bouncing system ends.
Professional Front fork:
Travel: The maximum length the fork can compress. XC uses 80-120mm. Fork 130-160mm for trail and AM. Downhill to 180mm or more.
Rebound Rebound: After it bounces and shrinks to the extreme, the medium (resistance glue, spring, air) bounces back to the original stroke length, that is, the second half of the bounce Spring, because the rebound speed is affected by the oil damping, so the separate become a professional term.
Resistance Damping: When rebounding, how fast the rebound speed is determined by the resistance. Under high-speed driving, the rebound is fast, and it will be bounced; the rebound is slow, and the stroke is shortened when there are continuous obstacles, and the feel is the same as a hard fork without rebound.
Rebound Adjustment: This is a technical selling point, and a fork with this function is a few hundred dollars more expensive. But Marzucci’s classic fork Z3 has this function; in addition, RockShox’s fork, as long as the model is followed by SL, also has this function. As the name implies, it adjusts the speed of the rebound. The fork with this function can achieve the purpose of adjusting the rebound without changing the clear and thick oil. The impact of rebound adjustment in off-road – small stone roads and dirt roads, need to rebound faster; rocks and roads with large drop need to rebound slower. The rebound adjustment knob is generally on the left side of the fork. The principle is that after the rotation, the oil hole can be made smaller, and the oil throughput per unit time can be reduced, the oil output time can be prolonged, and the rebound can be slowed down. The same principle as the plastic salt shakers with holes in restaurants. According to Chinese thinking habits, it is easier to understand rebound adjustment as resistance adjustment, because the speed of rebound is controlled by the amount of oil resistance in and out.
Lockout: When riding, the front fork can be locked through a special knob. Like a hard fork, there is no shock absorption response to any obstacles. This reduces slack, makes climbing easier, and saves effort on long rides. The use of ordinary players is not obvious, it is recommended to spend money on other components. There are two types of locking structures, one is mechanical locking and the other is damping locking.
Braking System
The braking system includes brakes, brake levers, and brake lines.
Mountain bikes use two kinds of brakes: [V brakes], [disc brakes], and the [hanging brakes] of ordinary bicycles are not common.
V-brake: The force is very large, because it is braked by the friction rim, so the rim must be adjusted in place, and it is not easy to deform.
Disc brakes: Compared with V brakes, it is more difficult to lock the tires. When driving at high speed, locking is very dangerous, which will cause sideslip and rollover. The price of disc brakes is very expensive, and the better ones are around 1,000 yuan. For 400 yuan, V brakes can be quite good.
There are two types of disc brakes: hydraulic disc brakes and mechanical disc brakes. Hydraulic disc brakes rely on oil to press the brake pads to obtain a huge braking force. This type of brake is very common on downhill bikes; wire-pulled disc brakes rely on fingers. The power to brake, in fact, is more than enough for XC.
There are also two types of V-brakes: hydraulic V-brakes and mechanical V-brakes. The principle of pressing the brake pads is the same as that of the two disc brakes. It’s just that hydraulic V-brakes are not very common. They are too easy to lock, so they are hardly used in cars.
Transmission system
The transmission system includes a crankset, a central axle, a chain, and a flywheel.
Crankset: Also called sprocket. Most of them have 3 gears. Some people change to 2 gears when they are looking for light weight, but some CNC have 4 gears, but this is a bit uncomfortable. Usually our crankset is 44-32-22T, but the crankset with 3*10 speed is 42-32-24.
Bottom bracket: There are three types of bottom brackets: one-piece bottom bracket, plum hole bottom bracket and square hole bottom bracket. The length and diameter also have different standards and must be purchased according to the corresponding crankset.
Chain: This is a consumable item. It is common to break the chain. If you ride a long distance, you must bring a spare to avoid hitchhiking on the Qinghai-Tibet road.
Cassette: This is a choice. There are 8-speed 24-speed, 9-speed 27-speed, and 10-speed 30-speed. SRAM even has an 11-speed cassette. In fact, the driver will not use all the gears, only one gear is used 80% of the time, and this gear must be the most suitable for the driver’s pedaling intensity and frequency. It can be seen that the more gears the transmission system, the more precise the driver can choose the gear that suits him. The 27-speed has three more gears than the 24-speed, giving the driver more options. And the more gears, the smoother the shifting.
Shifting system
The shifting system includes shifting levers, front derailleurs, rear derailleurs, and shifting cables.
Transmission, the two most common brands in China, one is Shimano (Japan), and the other is SRAM (United States).
SRAM is one of the originators of shifting production, designed for rigidity and durability over refinement. Shimano is the only manufacturer that can compare to SRAM in the mountains, and its high-end products can be called handicrafts. The two have occupied the Chinese market for many years, and SRAM is indeed superior in terms of cost performance. For example, the SRAM X9 shifting system is designed for Shimano Deore XT, but the price is much cheaper. It should also be noted that some parts of Shimano and SRAM are not compatible (for example, the SRAM shifter cable ratio is 1:1, while the Shimano is 1:2.5), it is best not to mix.
Shifter: There are two types, one is the shifter, the other is the shifter, the shifter is faster when changing gears, some people love shifter, and it varies from person to person. Most of Shimano’s derailleurs are derailleurs, and SRAM’s handlebars are famous.
There is also a dual-control gear shift, which integrates the switch and the brake handle. The advantage of this is that it has high compatibility and aesthetics. The disadvantage is that if the brake handle is broken, the switch is not broken. All have to be replaced. In addition, operating the brake and shifting at the same time has a great hidden danger to safety, and the dual-control system has basically withdrawn from the market in the field of mountain bikes.
Front derailleur: go to XT for those with more money, Alivio for 9-speed cars with less money, and Deore for 10-speed cars.
Rear derailleur: It is more important than the front derailleur. It is recommended to install a guy with a higher grade than the front derailleur. For example, Shimano’s SLX, Deore XT series, SRAM X9, etc., are strong and durable. For less money, install Shimano Alivio for 9-speed and SRAM X5 for 9/10-speed.
Shift cable: Thinner than brake cable.
Wheel
Wheels include rims, steel wires, front and rear axles, tires, and inner tubes.
Rims: Mountain bikes should use double-layer rims. Because the double-layer ring is stronger than the single-layer ring, it can better withstand the test of the performance of the bicycle in the harsh terrain. The rim is divided into: knife ring and I-shaped ring.
The advantage of the knife ring is that it has strong resistance to longitudinal impact, and no circumferential deformation will occur no matter how strong the strength is, while the lateral deformation is well adjusted; the knife ring can also reduce air resistance, which is suitable for amateur drivers and training. The disadvantage is that it is heavy and not suitable for climbing.
The I-shaped ring has a stronger resistance to lateral impact.
Steel wire (spoke): There are two kinds, one is ordinary, the cross section is round; the other is flat cross section (wind resistance strip), which can reduce the wind resistance on the front.
Axle: Also known as hub. Friends who use disc brakes should choose the disc brake shaft, because the disc brake pads are fixed on the disc brake shaft; friends who use V brakes can use ordinary shafts. If you want to upgrade to disc brakes in the future, you can install the disc brake shaft first. .
The axles are divided into [Peilin] axles and [bead gear] axles. It is recommended to buy a bearing shaft, which can be replaced.
Tire: Important because it directly affects the rider’s handling of the bike on a specific road surface. Different tread patterns adapt to different road surfaces.
The flatter the tread, the lower the resistance, the faster the speed and the stronger the friction on the flat ground. Bald tires, suitable for smooth concrete roads in the city.
The more convex the tread, the greater the resistance, the slower the speed, and the stronger the friction on the mountain.
Inner tube: It is a consumable item.
Welcome to eWingFly Store buy as what you like and you want,enjoy your shopping.
